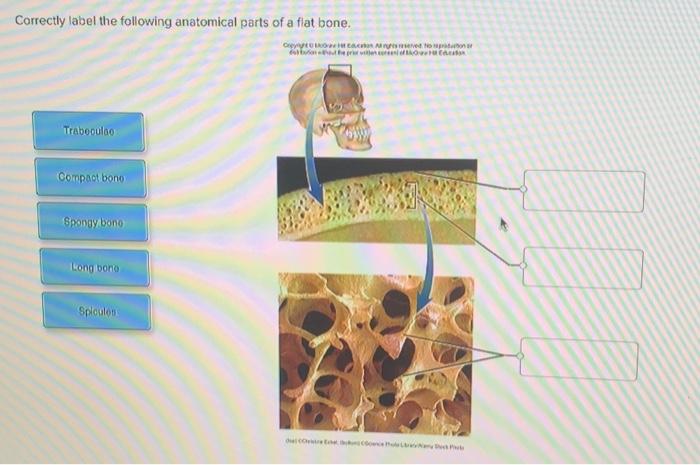
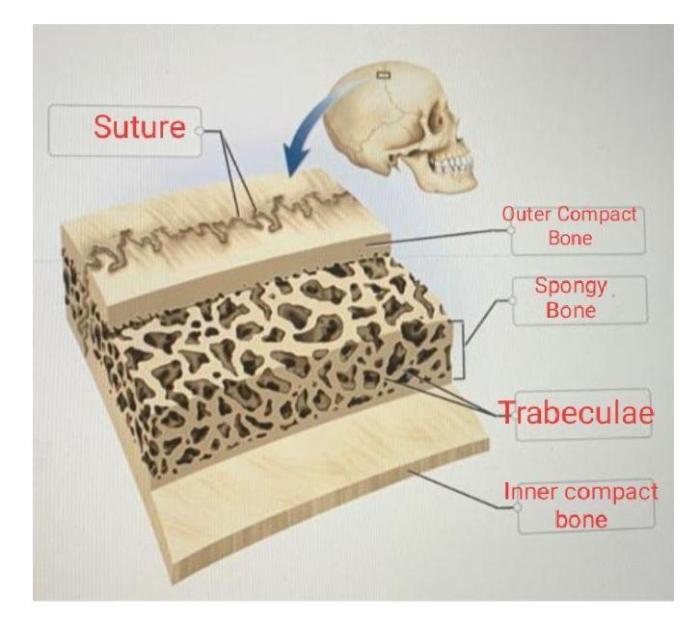
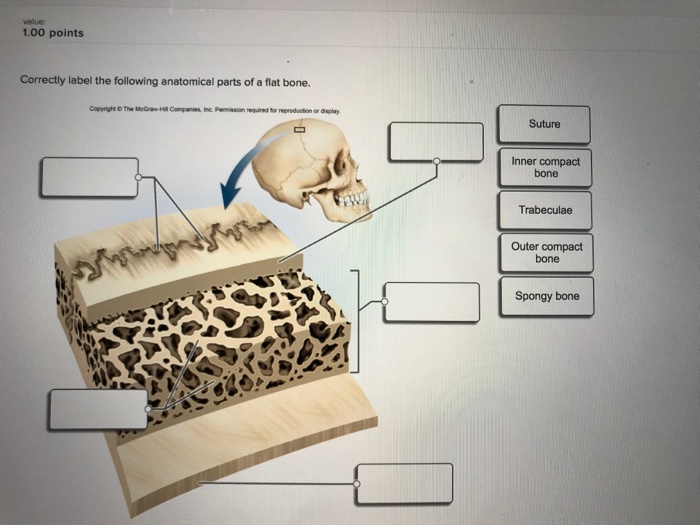
Correctly label the following anatomical parts of a flat bone – Correctly labeling the anatomical parts of a flat bone is essential for understanding its structure and function. Flat bones are thin, plate-like bones that form the skull, sternum, and pelvis. They provide protection, support, and attachment points for muscles.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the external and internal features of flat bones, including their margins, surfaces, processes, diploë, medullary cavity, and trabeculae. By understanding the anatomy of flat bones, we can better appreciate their role in the human body.
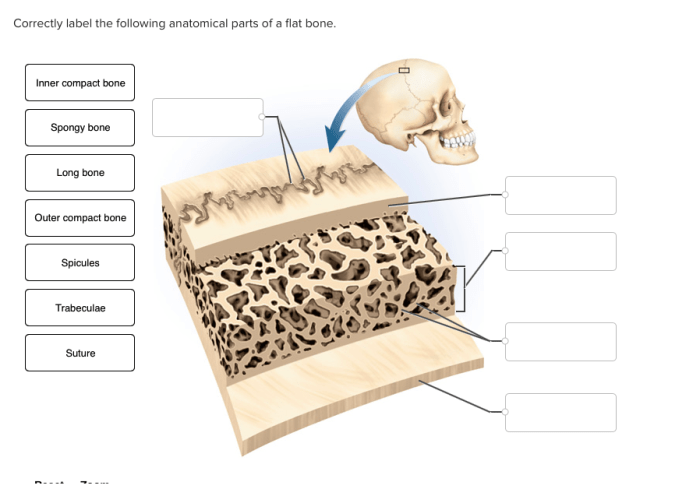
Anatomical Structure of a Flat Bone
Flat bones are thin, plate-like structures that provide protection, support, and attachment for muscles. They are composed of two compact bone layers sandwiching a layer of cancellous bone, forming a lightweight yet durable structure.
External Features of a Flat Bone, Correctly label the following anatomical parts of a flat bone
- Margins: The edges of a flat bone, which can be smooth, serrated, or irregular.
- Surfaces: The outer and inner surfaces of a flat bone, which can be flat, concave, or convex.
- Processes: Bony projections or extensions from the surface of a flat bone, which provide attachment for muscles or ligaments.
Internal Features of a Flat Bone
- Diploë: A layer of cancellous bone between the two compact bone layers.
- Medullary cavity: A central cavity within the diploë, which contains bone marrow.
- Trabeculae: Thin, bony struts that form the network of cancellous bone.
Blood Supply and Innervation of a Flat Bone
Flat bones receive their blood supply from arteries that enter through nutrient foramina on their surfaces. The arteries branch into capillaries that nourish the bone tissue. Flat bones are innervated by nerves that supply sensory and motor function to the bone and surrounding structures.
Examples of Flat Bones in the Body
- Skull: The flat bones of the skull protect the brain and provide attachment for facial muscles.
- Sternum: The flat bone that forms the anterior wall of the thorax, providing protection for the heart and lungs.
- Pelvis: The flat bones that form the bony basin of the pelvis, providing support for the abdominal organs and attachment for muscles.
Helpful Answers: Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Parts Of A Flat Bone
What are the main external features of a flat bone?
The main external features of a flat bone include its margins, surfaces, and processes. Margins are the edges of the bone, surfaces are the flat areas of the bone, and processes are projections or extensions of the bone.
What is the diploë?
The diploë is a layer of spongy bone located between the outer and inner tables of a flat bone. It is filled with red bone marrow and provides strength and support to the bone.
What is the function of the medullary cavity?
The medullary cavity is a hollow space located within the center of a flat bone. It contains yellow bone marrow and provides a space for blood cell production.